Введение
В мире растет число лекарственно-устойчивых бактериальных и грибковых инфекций, поэтому все большее значение приобретает разработка альтернативных вариантов уничтожения их возбудителей. Все более важным представляется создание устойчивых физических или иных методов, позволяющих устранить таких проблемных возбудителей.
К подобным методам относится терапия низкотемпературной атмосферной плазмой (CAPP), обладающая подтвержденной эффективностью лечения антибиотикорезистентных бактериальных, вирусных и грибковых инфекций (1-5).
Этот метод также корригирует и повышает уровень ряда факторов, способствующих заживлению и ускоряющих его, что может быть особенно эффективно при нарушениях заживления ран (6, 7). Первоначально CAPP применяли в медицине человека, но в настоящее время она получает все более широкое признание в ветеринарии, отчасти благодаря безболезненности и возможности применять ее без седации (8), хотя исследований на животных в настоящее время недостаточно, поскольку метод малоизучен.
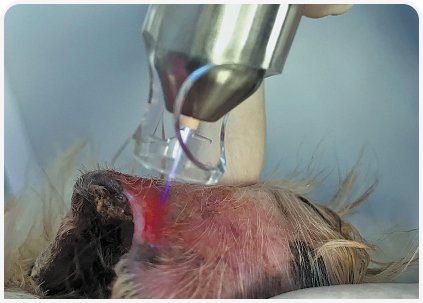
В статье представлены общие данные об этом методе терапии и несколько практических примеров его эффективного применения в клиниках для мелких животных (Рисунок 1).
Основные физические принципы и принцип действия
Плазму иногда называют «четвертым агрегатным состоянием материи» (после твердого, жидкого и газообразного); по сути, это газообразная смесь свободных ионов или электронов в ограниченном пространстве (9). Природные примеры этого явления включают молнии и солнечные вспышки, но плазма может быть получена и искусственно при комнатной температуре и нормальном атмосферном давлении, например путем ускорения заряженных газообразных частиц электромагнитным полем.
Показано, что CAPP-терапия ускоряет процесс заживления и уменьшает образование рубцов. Механизм ее действия пока изучен не полностью, хотя известно, что CAPP активно влияет на определенные факторы роста (например, FGF-7 для миграции кератиноцитов), противовоспалительные сигнальные молекулы (например, TGF-b) и воспалительные сигнальные пути (6-11).
Изначально метод CAPP предназначался для дезинфекции ран и ускорения заживления у людей, пострадавших от ожогов, но сейчас показания к его использованию расширены на многие другие клинические ситуации. Он эффективен при лечении как простых, так и осложненных кожных инфекций (особенно вызванных возбудителями с множественной лекарственной устойчивостью), а также при различных других нарушениях заживления ран, например при диабете (1, 3, 6).

По многочисленным данным, эта терапия высокоэффективна при борьбе с бактериальными, вирусными и грибковыми возбудителями, даже при наличии биопленок (2, 3, 5, 9), а ее физический механизм действия означает, что любая устойчивость возбудителей к антибиотикам, антимикотикам или противовирусным препаратам не имеет значения. Исследования показали, что CAPP обладает отличным бактериостатическим эффектом в отношении метициллин-резистентных Staphylococcus aureus spp (MRSA), S. pseudintermedius (MRSP) и Pseudomonas aeruginosa с множественной лекарственной устойчивостью (MRPA), одних из самых распространенных бактериальных возбудителей кожных инфекций в ветеринарии (1-4).
Конструкция и применение устройств
В настоящее время существует три основных типа устройств, каждый из которых имеет определенные преимущества и недостатки. Все они предполагают создание низкотемпературной плазмы путем ионизации газа до состояния плазмы: обычно атмосферного воздуха (т. е. кислорода и азота) либо инертного газа (например, аргона).
1. Наиболее простой и дешевый тип (от 2000 евро) создает электрический заряд на катоде устройства и использует в качестве анода кожу, при этом плазма генерируется в узком пространстве между ними (Рисунок 2). Его основными преимуществами (помимо стоимости) являются легкость использования и сравнительно простая конструкция, позволяющая питать устройство от батарей. Однако некоторые пациенты реагируют на шум или ощущение «покалывания», выраженность которого зависит от силы тока.
2. Второй тип устройств использует промежуточную среду (например, пену), помещенную между катодом и кожей в качестве проводника электричества. Это уменьшает или устраняет ощущение покалывания (Рисунок 3), хотя прямой контакт с раной все еще может восприниматься некоторыми пациентами как неприятный. Этот метод позволяет обрабатывать относительно большую площадь поверхности и экономит время при лечении крупных ран или крупных собак. Однако у небольших пациентов, при лечении небольших ран или при поражении кожных складок пену трудно разместить правильно, что может затруднить применение устройства. Кроме того, для каждого пациента требуются новые подушечки и, хотя устройства портативные, для их работы требуется питание от сети.
3. Третий тип устройств генерирует плазму из инертного газа, такого как аргон, и затем выпускает через кончик ручки в виде небольшой струи пламени (Рисунок 1). Струю проводят по поверхности кожи круговыми движениями, близко, но не касаясь самой раны. Такая конструкция позволяет проводить выборочную «точечную» обработку, даже в глубоких складках кожи или раневых полостях, и обеспечивает быстрое высушивание мокнущих и гнойных ран с минимальным раздражением или шумом. Недостаток заключается в высокой стоимости (до 15 000 евро), потреблении газа и весьма ограниченной портативности устройства.
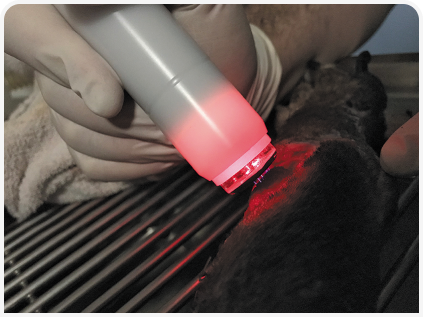
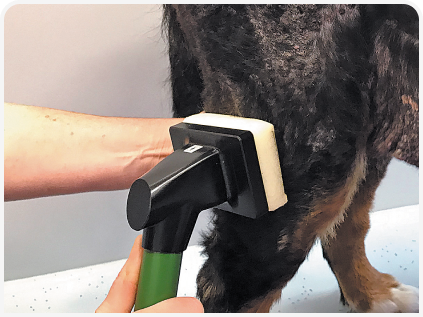
Все три устройства просты в использовании и могут применяться ассистентами после краткого инструктажа, что позволяет удобно интегрировать терапию CAPP в ежедневную практику в условиях нестерильного консультационного кабинета либо в асептической операционной. Поскольку терапия безболезненна, седация или анестезия пациенту требуются редко, хотя эффективность лечения, безусловно, зависит от выявления первопричины заболевания (6, 7).
Продолжительность и частоту применения подбирают в зависимости от технических характеристик устройства (глубина проникновения составляет от нанометров до нескольких миллиметров), а также от типа, глубины и характера поражения. Как правило, пораженный участок обрабатывают каждые 2-3 дня в течение двух недель, а затем один раз в неделю.
На сегодняшний день побочные эффекты у CAPP минимальные, за исключением незначительного раздражения кожи при длительном контакте с ней (8). Несмотря на то, что сравнительных исследований эффективности различных устройств немного (12), автор считает, что переносимость пациентами и скорость заживления лучше у третьей конструкции. В любом случае владельцы животных, как правило, очень довольны результатами применения любого из устройств CAPP и готовы нести дополнительные расходы, связанные с этой терапией.
Эксперт-квиз по диагностике зуда
Возможное применение в ветеринарной медицине
В настоящее время все устройства предназначены в основном для местного применения, и наиболее важным и инновационным аспектом CAPP-терапии являются возможность физической дезинфекции практически любого участка тела с бактериальным, вирусным или грибковым поражением (1, 4, 5) и высокая эффективность в отношении как нерезистентных, так и устойчивых штаммов бактерий (1, 12). Учитывая ограниченное проникновение в ткани, идеальной областью применения этого метода представляются открытые неглубокие раны; его положительный эффект в труднодоступных участках тела (например, межпальцевые промежутки, полости тела, слуховые проходы, глубокие раны) более сомнителен.
По крайней мере в настоящее время многое зависит от конструкции устройства и типа обрабатываемого поражения, поэтому некоторые устройства CAPP могут быть применимы для лечения пододерматита или наружного отита, в то время как другие более эффективны для использования на больших поверхностях.
Помимо дезинфекции, у этого метода терапии есть и другие преимущества. Его все чаще используют при васкулитах, например при лейшманиозе. На Рисунке 4 показано поражение у лабрадора, ранее получившего четырехнедельный курс терапии меглумина антимониатом, милтефозином и аллопуринолом. Хотя клинические показатели и титры антител показывали хороший ответ на лечение, сопутствующий васкулит привел к постепенному утяжелению изъязвления с внутренней стороны шиловидного отростка и к обнажению хряща. В течение 28 дней терапии CAPP удалось добиться почти полной ремиссии, хотя через шесть месяцев из-за сопутствующего лейшманиоза проявления заболевания развились вновь.
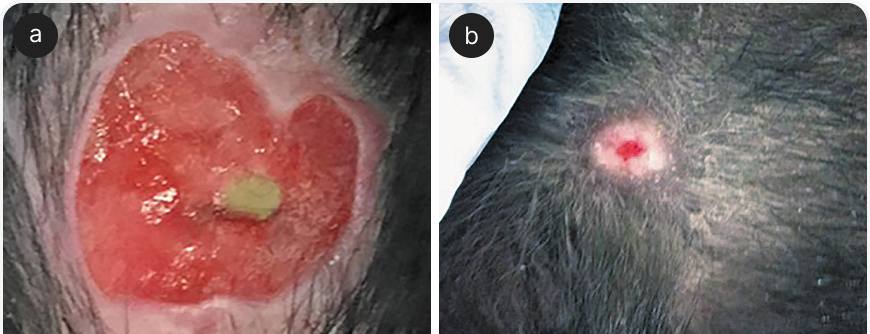
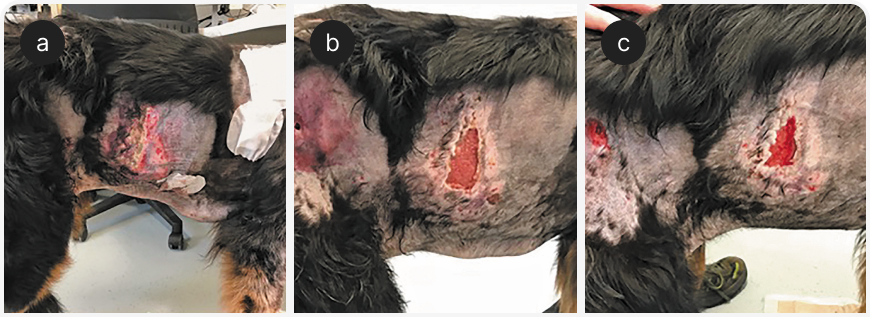
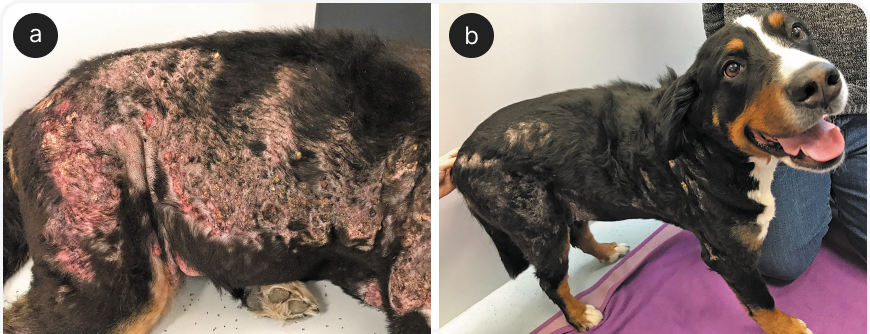
Важно отметить, что, хотя CAPP способствует заживлению раны, если не лечить основное заболевание, например, у пациентов с иммуносупрессией, возможен ранний рецидив (13). На Рисунке 5 показана восьмилетняя собака породы бернский зенненхунд, у которой из-за некротизирующей непроходимости кишечника вследствие инородного тела развилась септицемия.
У собаки ранее был диагностирован гипоадренокортицизм, и в течение нескольких лет она получала лечение дезоксикортикостероном. В результате септицемии у нее развились несколько очагов некротизирующего фасциита на боковых поверхностях тела, слабо ответивших на тройную антибиотикотерапию, предположительно вследствие лечения кортикостероидами. Однако применение CAPP привело к быстрому улучшению в течение трех недель, и, хотя за это время у собаки появились дополнительные очаги фасциита, они также были успешно вылечены, и через 24 дня после лечения все поражения купировались без дальнейших рецидивов.
Метод CAPP также оказался полезен при ряде иммуноопосредованных заболеваний. Это показано на Рисунке 6, где изображена трехлетняя немецкая овчарка с перианальными свищами.
Собака получала лечение комбинацией CAPP, циклоспорина и такролимуса местно, но для сравнения обработали CAPP только левую половину заднего прохода, а правую во время сеансов холодноплазменной терапии закрывали бумагой.
Через 18 дней стало видно, что, несмотря на эффективность медикаментозного лечения, рана с левой стороны закрылась значительно быстрее, а рубцов осталось меньше, чем на другой стороне.
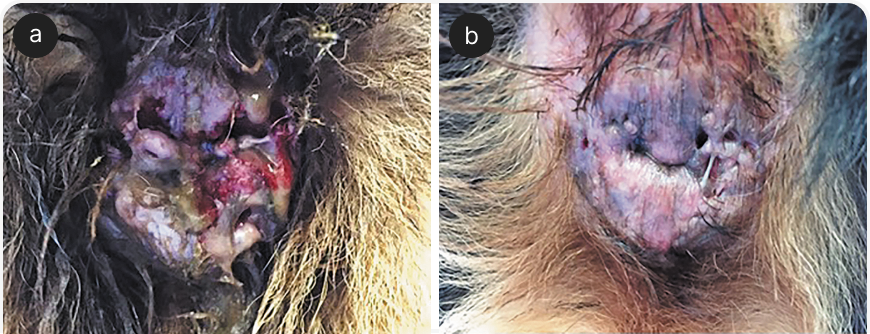
Другой актуальной темой является благоприятное влияние холодноплазменной терапии на фиброз (11). На Рисунке 7 показана четырехлетняя собака породы бернский зенненхунд с тяжелым кальцинозом кожи, вызванным ятрогенным гиперадренокортицизмом в результате лечения листовидной пузырчатки.
Возможности лечения пузырчатки в таких случаях очень ограничены и в основном включают местную противовоспалительную терапию (например, ДМСО) и переход с глюкокортикоидов на альтернативные препараты, такие как циклоспорин. Подкожный кальциноз часто может привести к значительному рубцеванию, но в данном случае лечение CAPP привело к очень быстрой реакции: 90% кожи полностью зажило без рубцов в течение четырех недель, шерсть впоследствии полностью отросла.
Наконец, на данный момент CAPP может найти применение и в других областях. Уже проводят исследования применения этого метода внутри полостей организма с помощью минимально инвазивных вмешательств (например, эндоскопии) (14). Его использование в хирургии все еще спорно; он может быть полезен для дезинфекции послеоперационной раны и предотвращения образования рубцов, но возможность его интраоперационного использования не определена. Метод может снизить бактериальную нагрузку после операции, но длительное время применения и увеличение продолжительности операции может привести к потере жидкости из тканей, что приведет к ухудшению заживления (11, 15).
Заключение
Терапия низкотемпературной атмосферной плазмой (CAPP) — несложный физический метод лечения, позволяющий значительно ускорить заживление многих кожных ран. Метод эффективно уничтожает возбудителей инфекции независимо от наличия лекарственной устойчивости и ускоряет выздоровление пациента, особенно при наличии факторов, замедляющих заживление. Поскольку применение препарата быстрое, безболезненное и несложное, он удобен для ежедневного использования
в ветеринарной практике, хотя окончательная объективная оценка его эффективности пока отсутствует. Важно отметить, что CAPP-терапия не должна заменять тщательную ветеринарную диагностику, поскольку не позволяет излечить основное заболевание.
Терапия низкотемпературной атмосферной плазмой (CAPP) — несложный физический метод лечения, позволяющий значительно ускорить заживление многих кожных ран. Метод эффективно уничтожает возбудителей инфекции независимо от наличия лекарственной устойчивости и ускоряет выздоровление пациента, особенно при наличии факторов, замедляющих заживление. Поскольку применение препарата быстрое, безболезненное и несложное, он удобен для ежедневного использования в ветеринарной практике, хотя окончательная объективная оценка его эффективности пока отсутствует. Важно отметить, что CAPP-терапия не должна заменять тщательную ветеринарную диагностику, поскольку не позволяет излечить основное заболевание.
-
1.Daeschlein G, Napp M, von Podewils S, et al. In vitro susceptibility of multidrug resistant skin and wound pathogens against low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma jet (APPJ) and dielectric barrier discharge plasma (DBD). Plasma Process Polym 2014;11(2):175-183.
-
2.Hüfner A, Steffen H, Holtfreter B, et al. Effects of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma and sodium hypochlorite solution on Enterococcus faecalis biofilm: an investigation in extracted teeth. Plasma Process Polym 2017;14(3):1600064.
-
3.Koban I, Matthes R, Hübner N-O, et al. Treatment of Candida albicans biofilms with low-temperature plasma induced by dielectric barrier discharge and atmospheric pressure plasma jet. NJP 2010;12(7):073039.
-
4.Kondeti VSK, Phan CQ, Wende K, et al. Long-lived and short-lived reactive species produced by a cold atmospheric pressure plasma jet for the inactivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Free Radic Biol Med 2018;124:275-287.
-
5.Sun P, Sun Y, Wu H, et al. Atmospheric pressure cold plasma as an antifungal therapy. Appl Phys Lett 2011;98(2):021501.
-
6.Hasse S, Duong Tran T, Hahn O, et al. Induction of proliferation of basal epidermal keratinocytes by cold atmospheric pressure plasma. Clin Exp Dermatol 2016;41(2):202-209.
-
7.Schmidt A, Bekeschus S, Wende K, et al. A cold plasma jet accelerates wound healing in a murine model of full-thickness skin wounds. Exp Dermatol 2017;26(2):156-162.
-
8.Daeschlein G, Scholz S, Ahmed R, et al. Cold plasma is well-tolerated and does not disturb skin barrier or reduce skin moisture. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2012;10(7):509-515.
-
9.Filipić A, Gutierrez-Aguirre I, Primc G, et al. Cold plasma, a new hope in the field of virus inactivation. Trends Biotechnol 2020;38(11):1278-1291.
-
10.Haertel B, Eiden K, Deuter A, et al. Differential effect of non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma on angiogenesis. Lett Appl NanoBioScience 2014;3(2):159-166.
-
11.Metelmann HR, Vu TT, Do HT, et al. Scar formation of laser skin lesions after cold atmospheric pressure plasma (CAP) treatment: a clinical long-term observation. Clin Plasma Med 2013;1(1):30-35.
-
12.Arndt S, Schmidt A, Karrer S, et al. Comparing two different plasma devices kINPen and Adtec SteriPlas regarding their molecular and cellular effects on wound healing. Clin Plasma Med 2018;9(10):1016.
-
13.Classen J, Dengler B, Klinger CJ, et al. Cutaneous alternariosis in an immunocompromised dog successfully treated with cold plasma and cessation of immunosuppressive medication. Tierärztl Prax K 2017;45(05):337-343.
-
14.Winter J, Nishime TM, Bansemer R, et al. Enhanced atmospheric pressure plasma jet setup for endoscopic applications. J Phys Appl Phys 2018;52(2):024005.
-
15.Nolff MC, Winter S, Reese S, et al. Comparison of polyhexanide, cold atmospheric plasma and saline in the treatment of canine bite wounds. J Small Anim Pract 2019;60(6):348-355.




 332
332  20 мин
20 мин





.png)





